PEPs & Sanctions Screening
Global PEPs & Sanctions Screening Solution
Stay ahead of potential risks, including PEPs (Public Exposed People), by receiving instant alerts about critical changes to your customers’ risk status, allowing you to take timely action to mitigate any threats.
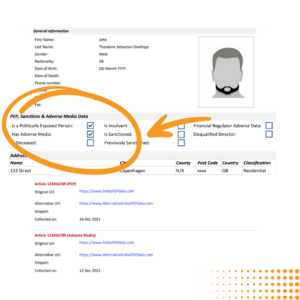
Global PEPs & Sanctions Screening Solution
Stay ahead of potential risks, including PEPs (Public Exposed People), by receiving instant alerts about critical changes to your customers’ risk status, allowing you to take timely action to mitigate any threats.
Why Choose PEPs and Sanctions Screening with Muinmos?
Ensure Compliance
Our advanced screening solution helps you meet regulatory requirements by identifying Politically Exposed Person (PEPs) and individuals under sanctions, ensuring your business operates within legal boundaries, sourced directly from authoritative databases.
Protect Your Regulation
By screening for PEPs and Sanctions, you safeguard your company's reputation from association with high-risk entities, maintaining trust with clients and partners.
Global Coverage
With our comprehensive global coverage, you can confidently onboard clients from around the world while staying compliant with international regulations.
Proactive
Risk
Stay ahead of potential risks by receiving instant alerts about critical changes to your customer's risk status, allowing you to take timely action to mitigate any threats.
Peace of Mind
With Muinmos' PEPs and Sanctions screening solution, you can have peace of mind knowing that you are effectively managing regulatory compliance and protecting your business from reputational damage.
Secure Client Onboarding with Muinmos:
Comprehensive KYC Verification
PEPs and Sanctions
Ensures compliance by screening clients against Politically Exposed Person (PEP) and sanctions lists worldwide.
Ongoing Monitoring
Continuously monitors clients to ensure ongoing compliance with regulations and mitigate risks.
Adverse Media
Identifies any negative news or information associated with clients across global media sources.
Liveliness
Validates the authenticity of client-provided identification documents and addresses through facial recognition technology.
FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions about Muinmos' PEPs and Sanctions Screening:
Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs) is someone who has held a significant government position locally, regionally, nationally, or internationally. Muinmos' database covers high-ranking officials globally, offering valuable insights on PEPs and individuals at higher risk. Aligned with the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) guidelines, Muinmos ensures compliance with anti-money laundering measures.
Despite the potential risks associated with PEP, not all are involved in criminal activities. Nevertheless, legislation, such as the EU's 4th money laundering directive, mandates enhanced due diligence when dealing with PEP.
The Muinmos PEPs Definition and ranking is based on the FATF version:
1)
- Heads of state
- Members of the national executive
- Members of the national legislatures
- Senior officials of military and law enforcement
- Senior officials of national agencies
- Board members of central banks
- Senior judiciary officials (national level)
- Top-ranking officials of political parties
2)
- Board members of International Organizations (HIOs) & International Sports Federations
Ambassadors, high commissioners, and other top diplomatic positions
- Members of the regional executive
- Members of the regional legislatures
- Senior judiciary officials (regional level)
- Senior management and board of directors of state-owned businesses and organisations.
- Mayors and members of local government (sub-regional level).
Numerous regulations and best practices emphasize that politically exposed persons (PEPs) include not only current officeholders but also individuals who have previously held such positions. Muinmos adheres to a similar standard. Consequently, the Muinmos -database encompasses former PEPs alongside current ones.
Moreover, relatives and close associates of PEPs are categorised as PEPs and subject to risk assessment, as outlined in the FAQ section below.
Yes. The FATF recommendations also apply to relatives and close associates of prominent entities, as these are also viewed as a potential source of risk – given their connections with the PEPs.
Muinmos considers the following categories of family members relevant from a PEP screening perspective (but not limited to):
- Spouse/ partner (including a person who is considered by his national law as equivalent to a spouse)
- Siblings/ Half-siblings
- Children/ Step-children and their spouses and partners
- Parents/ Step-parents
If an entity belongs to any of the above categories, it will be ranked at the same level as the PEP it is associated with unless the family member in question is a PEP in his/her own right. In such cases, the political position held by the spouse will determine his or her classification.
Our PEP and sanctions coverage is global.
All PEPs Profiles are checked for updates daily.
As our database must adhere to various global screening requirements, we consistently apply the most stringent regulations. This means that even if some jurisdictions only require screening of current politically exposed persons (PEPs), we still flag former office holders as PEPs regardless of their exit date. Additionally, we assign a 'Remove date' to all former officeholders' profiles to indicate when they left office, ensuring transparency and accuracy in our data.
Sanctions refer to actions taken to limit the activities of certain individuals or nations. While adverse media involves using publicly available information to uncover negative details about potential customers, sanctions lists serve as a global database of restrictions.
These lists, which are maintained and published by governments and international organizations, help identify and shield entities from individuals involved in illegal activities. Known as personal sanctions, they are essential for customer due diligence (CDD). Sanctions checks offer an additional layer of protection for businesses by ensuring they do not engage with those who are legally barred from doing so.
Although businesses already perform data verification through watchlists and adverse media checks, sanctions checks are a vital part of identity verification. They help companies comply with Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations, reinforcing their commitment to legal and regulatory standards.
Sanctions were first introduced by the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) in 1966, and since then, numerous sanctions regimes have been established to safeguard international interests against:
- Global conflicts and escalations
- Nuclear proliferation
- Terrorism and human rights abuses
Individuals, organizations, or governments may be added to these lists due to various illegal activities. Besides the general issues mentioned, these activities can also include money laundering, drug trafficking, and breaches of international treaties.
Entities on sanctions lists face financial penalties such as asset freezes and fines, along with other measures, which can range from reductions in military assistance to complete travel bans from their country.
In regulated sectors, especially in financial services, it is mandatory to perform PEPs (Politically Exposed Persons) and sanctions screening as part of the customer due diligence (CDD) process during onboarding. Depending on the outcomes of these screenings, additional checks may be necessary before deciding to proceed with onboarding a customer. These CDD activities are a key component of the broader Know Your Customer (KYC) process. For a deeper understanding of KYC, refer to our blog on the topic.
Sanctions, imposed by entities like the US, UK, EU, and international bodies such as the United Nations, are designed to prevent business interactions with certain countries, organizations, or individuals. According to the UK government, the objective of sanctions is "to influence the behavior of targeted regimes, individuals, or groups in a manner that improves conditions within that country.
There are numerous sanctions lists managed by different authorities. For example, the US Department of the Treasury’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) maintains the CAPTA (Correspondent Account or Payable-Through Account) sanctions list. Additionally, the EU and the UK each have their own distinct lists.
As stated on the US Treasury Department's website: "Every transaction involving a US financial institution must comply with OFAC regulations. If a bank is aware, or should be aware, that a transaction involves a sanctioned party, processing that transaction would be unlawful.
For companies operating in multiple countries—whether through offices, branches, sales operations, or partnerships—it's crucial to monitor various sanctions lists to ensure compliance across different regions.
Sanctions lists are extensive, crossing borders and continents, and involve a complex array of political and diplomatic considerations that organizations must manage. To comply with global regulatory standards and customer due diligence (CDD) requirements, businesses depend on solutions that offer thorough, accurate, and current sanctions checks.
While it's theoretically possible for teams to manually review these lists, this method is labor-intensive, inefficient, and increases the risk of inadvertently engaging with sanctioned individuals or entities.
Automation not only simplifies the process for organizations but also enhances accuracy and adherence to international regulations. Automated systems validate applicant information against constantly updated global databases, ensuring a comprehensive and reliable view of each customer.
Software solutions continuously integrate data from various sanctions and information sources, with regular updates to ensure that sanctions checks are both current and reliable.
Financial services businesses should adopt a risk-based approach rather than a one-size-fits-all solution. This approach usually involves evaluating applicants during the Know Your Customer (KYC) process to determine whether Customer Due Diligence (CDD) or Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) is appropriate. For insights into the distinctions between CDD and EDD, see our blog.
To effectively manage PEPs and sanctions screening, many organizations are increasingly relying on automated watchlist services that provide real-time screening and keep track of updates to sanctions lists. These services generate reports during the onboarding process and, when needed, offer continuous monitoring to notify businesses of any changes in an individual’s status, including new sanctions after the initial review.
While automatic checks are ideal, it is also considered best practice to manually review customers whenever there are updates to sanctions lists or changes in the customer’s details. Additionally, including key individuals such as directors, beneficial owners, and third-party payees in the screening process is advisable to ensure comprehensive compliance.
Partnering with individuals or entities that appear on sanctions lists can lead to significant legal and financial penalties for organizations. Besides the risk of failing to comply with essential regulations such as KYC, AML, and 6AMLD, such associations can severely tarnish a company's reputation.
For businesses onboarding clients with potential links to sanctions lists, it's essential to apply Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD). EDD is a rigorous layer of scrutiny designed for high-risk customers, providing a deeper investigation to safeguard against potential regulatory and reputational risks.
Category Leader
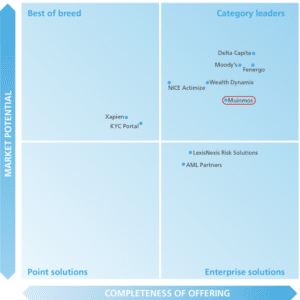
Chartis Research, a leading provider of research and analysis, crowned Muinmos as category leader in CLM Solutions for Wealth Management in 2023.
“Muinmos couples a deep understanding of customer pain points with a passion for overcoming these challenges, while its awards for integrated workflow and broker-dealer solutions reflect its understanding and focus.”
Nick Vitchev, Research Director at Chartis











